Real Nutritionist Degree Graduates. Honest Answers.
More Answers From Nutritionist Degree Graduates
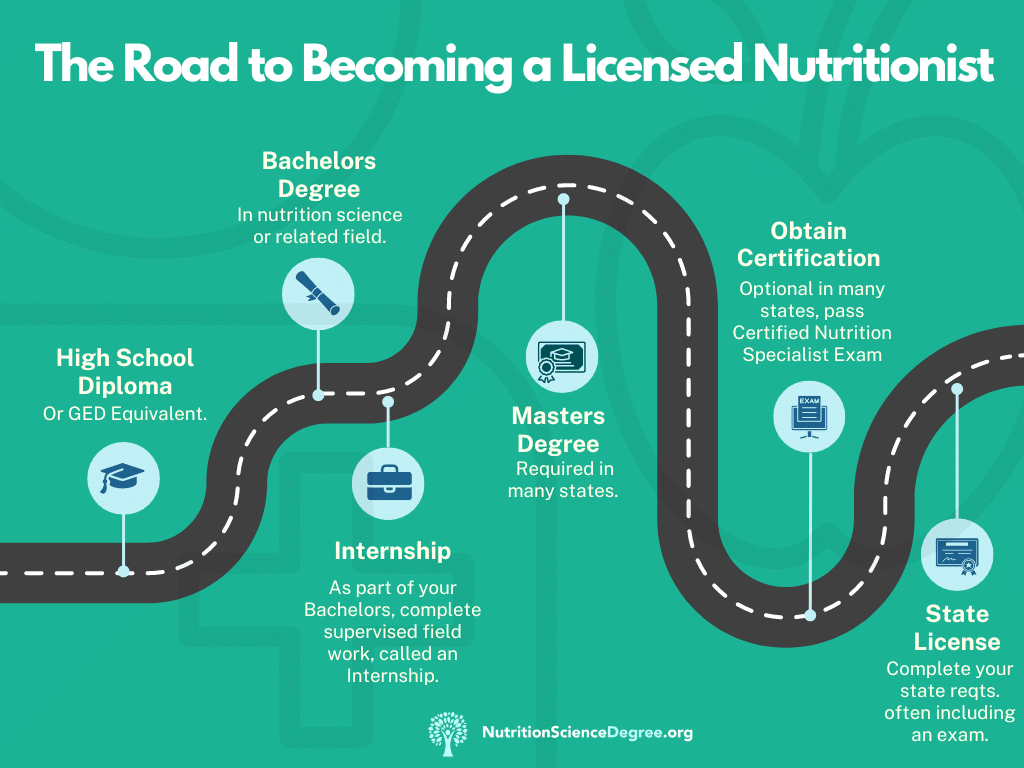
4 Steps to Becoming A Nutritionist
Step 1
Earn a Degree
Earn a Certificate, Bachelors or Masters in Nutrition.
Step 2
Internship
Complete a supervised internship.
Step 3
Certification Exam
In most states, certification requires passing the NANP Exam.
Step 4
Seek employment
Salary range, $40,630 – $97,330 (BLS 2020).
Want More Options? See Our Directory of Nutrition Degree Programs
What Our Experts Say About Online Nutrition Degree Programs
Nutrition science is how the body uses the food that you eat, and what impact that food and the nutrients within it have on your overall health and well-being, disease conditions, and health promotion.

Every dietitian is a nutritionist. However, not every nutritionist is a dietitian. A dietitian is a regulated and controlled title to have. So being a dietitian means that you completed a standardized set of education requirements. So across the board, all dietitians will have kind of completed this similar education and experience path, whereas a nutritionist on the other hand is not a regulated term, so this can vary widely then based on any experience or education that a person calling themselves a nutritionist folds.

An associate’s nutrition degree covers basic health and wellness topics. It could help you with some entry level jobs, I would assume it’s like health education or wellness, just kind of basic stuff where you could use that but not necessarily like the science based stuff as in-depth anyway.

Frequently Asked Questions
Education
What is Nutrition Science?
What Is A Nutrition Science Degree?
A nutrition degree, is the academic study of nutrition science, which looks at the connection between diet and health from a scientific perspective. It also examines the dietary habits and nutritional needs of people in order to establish an optimal way of maintaining health.
Increasingly, people have started taking charge of their health, and, as a result, nutrition scientists, nutritionists and dietitians are needed to assist patients with their food choices, diagnosing food related issues, and physical activity behaviors. If you have a passion for health and wellness, getting a degree in nutrition science might be an option.
What Is A Nutrition Science Degree?
What Is A Nutrition Degree?
A online nutrition degree is offered at the certificate, associates, bachelors, masters and PhD level. It focuses on the scientific study of nutrition and its impact on human health. It equips students with knowledge and skills related to food, nutrients, metabolism, and the role of nutrition in disease prevention and overall well-being. Common classes that are typically included in a nutrition science degree, are:
- Introduction to Nutrition: An overview of the principles of nutrition, including macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and fats) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals), digestion, absorption, and metabolism.
- Human Anatomy and Physiology: A study of the structure and function of the human body systems, including the digestive system, metabolism, and how nutrients are utilized.
- Biochemistry: An exploration of the chemical processes and reactions that occur within living organisms, with a focus on the biochemistry of nutrients, metabolism, and energy production.
- Food Science: An examination of the composition, processing, preservation, and safety of food, as well as the impact of cooking and storage on nutrient content.
- Nutritional Assessment: A study of methods used to assess nutritional status in individuals and populations, including dietary analysis, anthropometric measurements, and biochemical tests.
- Medical Nutrition Therapy: An in-depth look at the role of nutrition in managing and preventing chronic diseases, such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and obesity.
- Nutritional Epidemiology: An introduction to research methods used to study the relationship between nutrition and health outcomes, including the design and interpretation of nutritional studies.
- Sports Nutrition: A focus on the nutritional needs of athletes, including macronutrient and micronutrient requirements, hydration, and strategies for optimizing athletic performance.
- Community Nutrition: An exploration of public health nutrition, including nutritional needs of specific populations, nutrition education, and the development of community-based interventions.
- Food and Society: An examination of the social, cultural, and economic factors that influence food choices, food policy, and the global food system.
What Is A Nutritionist Degree?
What Is A Nutritionist Degree?
A nutrition science degree typically refers to a bachelors in nutrition science, as, in most states, becoming a nutritionist requires a bachelors level degree in the field of nutrition.
A nutritionist degree focuses on the scientific study of nutrition and its impact on human health. It equips students with knowledge and skills related to food, nutrients, metabolism, and the role of nutrition in disease prevention and overall well-being. Common classes that are typically included in a campus or online nutritionist degree, are:
- Introduction to Nutrition: An overview of the principles of nutrition, including macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and fats) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals), digestion, absorption, and metabolism.
- Human Anatomy and Physiology: A study of the structure and function of the human body systems, including the digestive system, metabolism, and how nutrients are utilized.
- Biochemistry: An exploration of the chemical processes and reactions that occur within living organisms, with a focus on the biochemistry of nutrients, metabolism, and energy production.
- Food Science: An examination of the composition, processing, preservation, and safety of food, as well as the impact of cooking and storage on nutrient content.
- Nutritional Assessment: A study of methods used to assess nutritional status in individuals and populations, including dietary analysis, anthropometric measurements, and biochemical tests.
- Medical Nutrition Therapy: An in-depth look at the role of nutrition in managing and preventing chronic diseases, such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and obesity.
- Nutritional Epidemiology: An introduction to research methods used to study the relationship between nutrition and health outcomes, including the design and interpretation of nutritional studies.
- Sports Nutrition: A focus on the nutritional needs of athletes, including macronutrient and micronutrient requirements, hydration, and strategies for optimizing athletic performance.
- Community Nutrition: An exploration of public health nutrition, including nutritional needs of specific populations, nutrition education, and the development of community-based interventions.
- Food and Society: An examination of the social, cultural, and economic factors that influence food choices, food policy, and the global food system.
Nutrition Degree Options: Associates v. Bachelors v. Masters
Students interested in a campus or online nutrition science degree have a number of options, including certificate, diploma, associates, bachelors, masters and PhD, each of which opens up different career opportunities. Below is a brief description of the three most common nutrition science degree programs:
- Associate of Science in Nutrition: An AS in Nutrition (or Applied Nutrition, as it’s sometimes referred to) is a two-year degree that prepares graduates for entry-level positions in traditional health settings such as hospitals, private medical offices, and public health agencies, as well as integrative health and wellness organizations and companies.
- Bachelor of Science in Nutrition: A BS in Nutrition is a four-year program typically designed to prepare graduates to work as a Registered Dietician. Courses cover such topics as nutrition therapy, how to manage daily stress, and ways to incorporate physical activity into daily life. Graduates typically go on to work as a nutritionist, health educator, or coach, or as a health promotion consultant in schools, health care facilities, corporations, wellness facilities, or the fitness setting.
- Master of Science in Nutrition: An MS in Nutrition is a two-year program designed for students with a bachelor’s in a life or physical sciences, including registered dietitians (RD/RDN), registered nurses, and other healthcare professionals. Graduate-level programs in nutrition often include a research component and culminates in a thesis. Some schools offer a master’s degree in food science or health and wellness.
Can I Get A Nutrition Degree Online?
Yes. Given the increasing popularity of online nutrition degree programs, now seemingly every nutrition science degree is offered in a fully online format.
Due to the potential for cost savings and increased time flexibility, online nutrition science degree programs are increasing in popularity. Of note, when selecting an online nutrition science degree program, make sure that the accrediting body certifying the college or university is recognized by your state, so that you can seamlessly qualify for certification or licensing. Also, note that many online nutrition science degree programs still require a supervised internship component which in some cases can also be completed online, but in many cases is required to be completed in-person.
Pros & Cons of Online vs. Campus Programs
Getting a nutrition science degree online has both advantages and disadvantages, and so you need to know both before making a decision.
Pros to an Online Nutrition Degree Program:
There are four primary advantages to attending an online nutrition science degree program:
- Flexibility: The primary reason many students are initially attracted to an online nutrition science degree, is that it offers them the flexibility to take classes on their own schedule. For students who have a career or family responsibilities, the ability to take classes on their own schedule, including on weekends and in the evenings is essential.
- Cost: Due to the lack of brick and mortar infrastructure, the lack of room and board requirements, and economies of scale, many online nutrition science degree programs are able to offer significant tuition and overall cost savings to online students. Of note, however, each school varies so it’s important to compare colleges carefully.
- Degree Offerings: The popularity of online nutrition science degrees, means that students typically have a broader range of nutrition science programs to choose from, than if they were choosing merely from the brick and mortar college to which they applied. That means, students have the ability to specialize their nutrition science degree to their particular desired focus more easily.
- Self-Paced Learning: Some students want to race through their degree program, whereas others want to be able to go significantly slower due to family or work obligations. An online nutrition science degree is particularly well suited to enable both options.
Cons to an Online Nutrition Degree Program:
There are some significant drawbacks to getting a nutrition science degree online. These include:
- Lack of Personal Interaction: Online nutrition science programs have certainly improved in this regard as they’ve better incorporated video conferencing and chat features, however, there is no substitute for in-person interaction with professors and students, and undoubtedly something is lost there.
- Lack of Hands On Experience: While hands on learning is less important in nutrition science than in many degrees, the opportunity to work face to face with clients is lost in an online experience. Increasingly, however, online nutrition science degree programs are working with employers to provide in-person hands on experiential learning opportunities.
- Less Prestigious: There was a time when nutrition science degrees from an online university were regarded as inferior to a traditional brick and mortar college. Increasingly, however that is no longer the case. That said, some employers may still see the degrees as substantively different.
Career
Step-By-Step: How To Become A Nutritionist
How To Become A Licensed Nutritionist
Below is a step by step guide on how to become a licensed nutritionist:
To become a licensed nutritionist in your state, you would typically need to follow these steps:
- Obtain a Bachelor’s Degree: Earn a Bachelor’s degree in nutrition, dietetics, or a related field from an accredited institution. Ensure that your program is recognized by the Accreditation Council for Education in Nutrition and Dietetics (ACEND) or the accrediting body that your state requires.
- Complete Required Coursework: Fulfill specific coursework requirements set by your state’s Board of Examiners of Dietitians. The coursework typically includes subjects such as nutrition science, biochemistry, physiology, anatomy, and food science.
- Gain Practical Experience: Accumulate practical experience by completing a supervised practice program or internship approved by your state’s certifying body. The program should meet the minimum required hours of supervised practice.
- Apply for Your State’s Licensure Exam: Submit an application for examination with your state’s certification board. This involves providing documentation of your education, supervised practice, and transcripts. Upon approval, you will receive a notification of eligibility to take the licensure exam.
- Pass the Licensure Examination: Take and pass your state’s approved licensing examination. This exam is specifically designed for licensing nutritionists, is typically state specific, and assesses your knowledge and competency in the field.
- Submit the Application for Licensure: Once you have successfully passed the examination, you can submit the application for licensure to your state’s certifying body. Include the required documents, such as the examination results, transcripts, and application fee.
- Background Check and Jurisprudence Exam: Complete a background check if your state requires one. Additionally, many states require you to pass a Jurisprudence Exam, which tests your knowledge of the laws and rules governing the practice of nutrition in your state.
- Maintain Licensure: After obtaining your license, you will need to meet continuing education requirements to maintain your licensure. Typically this means completing a certain number of hours of continuing education every two years.
Note: Every state’s requirements to become a licensed nutritionist or dietitian are slightly different, so it’s important that you review your state’s requirements closely before making decisions such as, which nutrition science program to enroll in, or which certification exam to take.
Nutrition Science Certifications: What You Need To Know
Nutritionist Certification: What You Need To Know
There are a number of different professional certifications for campus and online nutrition degree graduates. These certifications are required to be licensed in some instances (e.g. dietitians) whereas in other instances, people pursue a certification because it brings them additional credibility and often a pay increase, but are otherwise optional.
If you want to learn more about each state’s requirements, and whether your state requires certification, you can view this resource from the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics for an overview of the status of licensure and certification statutes. Additionally, the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics also provides an overview of the dietetics practitioner state licensure provisions. Finally, the Commission on Dietetic Registration (CDR) is the most common credentialing body in the nutrition science field, and it awards credentials to individuals at entry, and specialty levels to those who have met specific standards for competency, so it’s worth looking further into.
For more information on these credentials and how to earn them, see the chart below with certification requirements.
| Name of Credential | Overview and Requirements |
|---|---|
| Registered Dietitians (RD) or Registered Dietitian Nutritionists (RDN) | RDs or RDNs are individuals who have: |
| Nutrition and Dietetics Technicians, Registered (NDTR) or a Dietetic Technicians, Registered (DTR) | NDTRs or DTRs are individuals who have: |
| Specialist in Pediatric Nutrition | Pediatric Nutritionists encourage healthy food choices for children from as early as infancy, and successfully meet the following criteria: |
| Specialist in Renal Nutrition | Renal Nutritionists are experts on diet and nutrition in kidney disease who successfully meet the following criteria: |
| Specialist in Gerontological Nutrition | Gerontological Nutritionist are experts in effective nutrition strategies for older adults who successfully meet the following criteria: |
| Specialist in Sports Dietetics | Sports Dietitians provide individual and team nutrition counseling to enhance the performance of athletes, and successfully meet the following criteria: |
| Specialist in Oncology Nutrition | Oncology Nutritionists advocate for the efficacy of nutritional intervention in cancer care, and successfully meet the following criteria: |
Dietitian vs. Nutritionist: What Are The Differences?
Are Dietetics And Nutrition Science The Same Thing?
The terms nutritionist and dietitian are sometimes used interchangeably but they are not equivalent. It’s important to know the differences between the two service providers, and what to look for when choosing one. The chart below outlines the major differences between the roles:
| Dietitians | Nutritionists |
|---|---|
| Overview: Dietitians are degree-qualified health professionals who promote nutritional well-being, treat disease, prevent nutrition-related problems, and provide practical, safe advice, based on current scientific evidence. | Overview: A nutritionist is a non-accredited title that may apply to somebody who has completed courses in nutrition and dietetics. They often work in private practices and deliver group nutrition and cooking classes. The term “nutritionist” is not protected by law in almost all countries. |
| Education: Dietitians hold a bachelor’s or master’s degree in nutrition and dietetics, including a certain period of practical training in different hospital and community settings. | Education: Nutritionists likely need to complete some formal coursework in nutrition-related subjects to qualify for employment. An advanced degree, however, can prepare students to work as educators and researchers in the nutrition field. |
| Credentials: Dietitians are registered with the Commission on Dietetic Registration (CDR) and called registered dietitians, or RDs. They may also be licensed by state. | Credentials: Only nutritionists registered with Commission on Dietetic Registration (CDR) may legally declare themselves as registered dietitians. |
| Job Duties: Dietitians translate scientific nutrition principles into useful information that can be used by clients to create dietary plans to help promote healthy lifestyles. Dietitians are especially supportive of patients with medical conditions that require individualized dietary plans. | Job Duties: Nutritionists work with people to develop a healthy relationship with food by determining their current nutritional status, and educating them regarding nutritional needs, restrictions, and supplements. |
What Are My Career Options In Nutrition Science?
What Are My Career Options In Nutrition Science?
Nutrition science is a relatively broad field that offers careers as wide ranging as clinical nutrition to public speaking to journalism. Below is an overview of the career types or categories available to individuals studying nutrition science:
| Type of Job | Job Description |
|---|---|
| Clinical Dietetics | Clinical Dietitians provide medical nutrition therapy for patients in institutions such as hospitals and nursing care facilities. They assess patients’ nutritional needs, develop and implement nutrition programs, and evaluate and report the results. |
| Food and Nutrition Management | Food and Nutrition Managers interpret nutritional data, apply nutritional principles to promote health, and ensure the safety and sanitation of food, equipment, and personnel to provide quality care. |
| Public Health Nutrition | Public Health Nutritionists are registered dietitians who implement nutrition policies and programs for health departments as well as design and carry out programs in the general community to promote physical fitness and nutrition. |
| Education and Research | Registered Dietitians in education and research create and write curriculum for state boards of education, Dairy Council, Cooperative Extension Worksite Wellness, teach nutrition and fitness to employees, and manage or assist with clinical protocols, interventions, or clinical trials. |
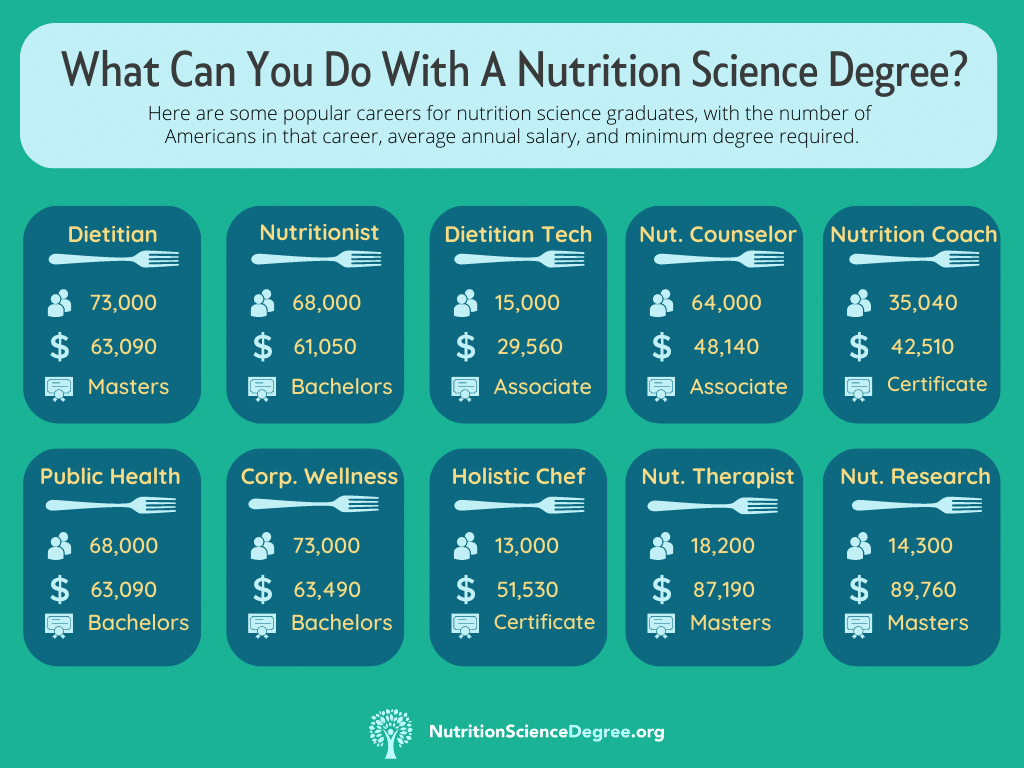
Most Popular Careers For Nutrition Degree Graduates
People with a nutrition degree have a wide range of career opportunities. However, the majority of people who get a campus or online nutrition science degree do one of the following:
- Registered Dietitian Nutritionist (RDN): Registered Dietitian Nutritionists are experts in nutrition and are qualified to provide medical nutrition therapy. They work in various healthcare settings, such as hospitals, clinics, and private practice. There are approximately 76,000 registered dietitians employed in the US.
- Clinical Dietitian: Clinical dietitians work in healthcare facilities, including hospitals, long-term care facilities, and outpatient clinics. They provide nutritional assessments, develop diet plans, and monitor patients’ nutritional status. There are approximately 32,000 dietitians employed in the US. (source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics).
- Community Nutritionist: Community nutritionists focus on improving the nutritional health of specific populations or communities. They work in public health settings, community organizations, and government agencies. The exact employment number for community nutritionists is difficult to estimate, but it is approximately 15,000.
- Food Service Manager: Food service managers with a background in nutrition science oversee food service operations in various settings, including hospitals, schools, and corporate cafeterias. The number of food service managers employed in the United States is estimated to be around 405,000.
- Corporate Wellness Coordinator: Corporate wellness coordinators develop and implement wellness programs in corporate settings, focusing on employee health and well-being. The exact employment number for corporate wellness coordinators is challenging to determine, but it is estimated at 30,000.
- Research Scientist: Graduates with a nutrition science degree can pursue research careers in academic institutions, government agencies, or private research organizations. The employment count for research scientists is estimated at approximately 20,000.
- Nutrition Consultant: Nutrition consultants provide expertise and advice on nutrition-related matters to individuals, organizations, or businesses. They may work independently or as part of a consulting firm. The employment number for nutrition consultants is estimated to be 150,000.
- Nutrition Educator: Nutrition educators work in schools, community centers, or nonprofit organizations, delivering nutrition education programs. The employment number for nutrition educators is approximately 40,000.
- Food and Nutrition Writer/Blogger: With a campus or online nutrition science degree, individuals can pursue careers as writers, bloggers, or content creators in the field of nutrition. The number of individuals employed specifically as food and nutrition writers or bloggers is 15,000.
Career Outlook for People With Nutrition Science Degrees
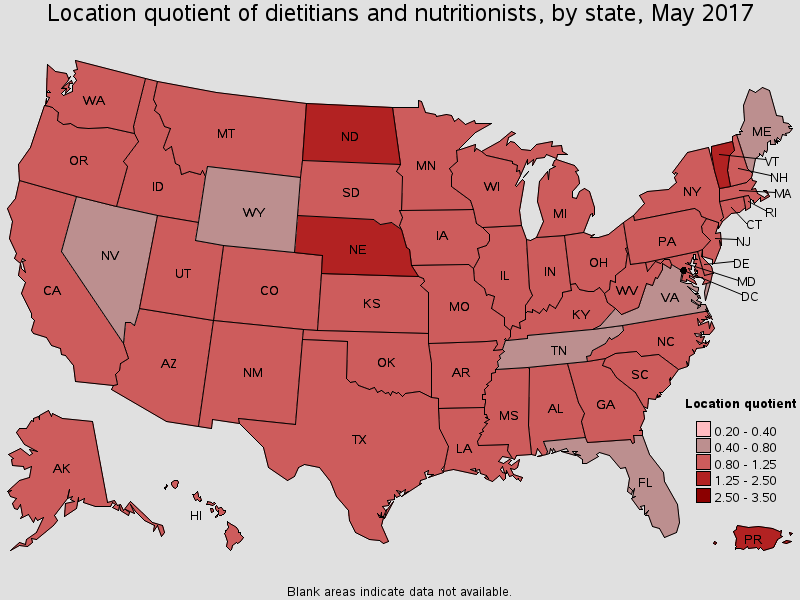
The job outlook for dietitians and nutritionists extremely positive. According to BLS Data, employment is projected to grow 15 percent from 2016 to 2026, much faster than the average for all occupations due to an increased interest in the role of food and nutrition, particularly preventative healthcare.
The BLS reports the states with the highest concentration of jobs and location quotients for dietitians and nutritionists in the map below (source: BLS.gov: Occupational Employment And Wages: Dietitians and Nutritionists, data for May 2017).
Explore More
Resources
Learn More About Nutrition Science Careers, Salary, Degrees & Hone Your Professional Skills By Visiting These Resources: